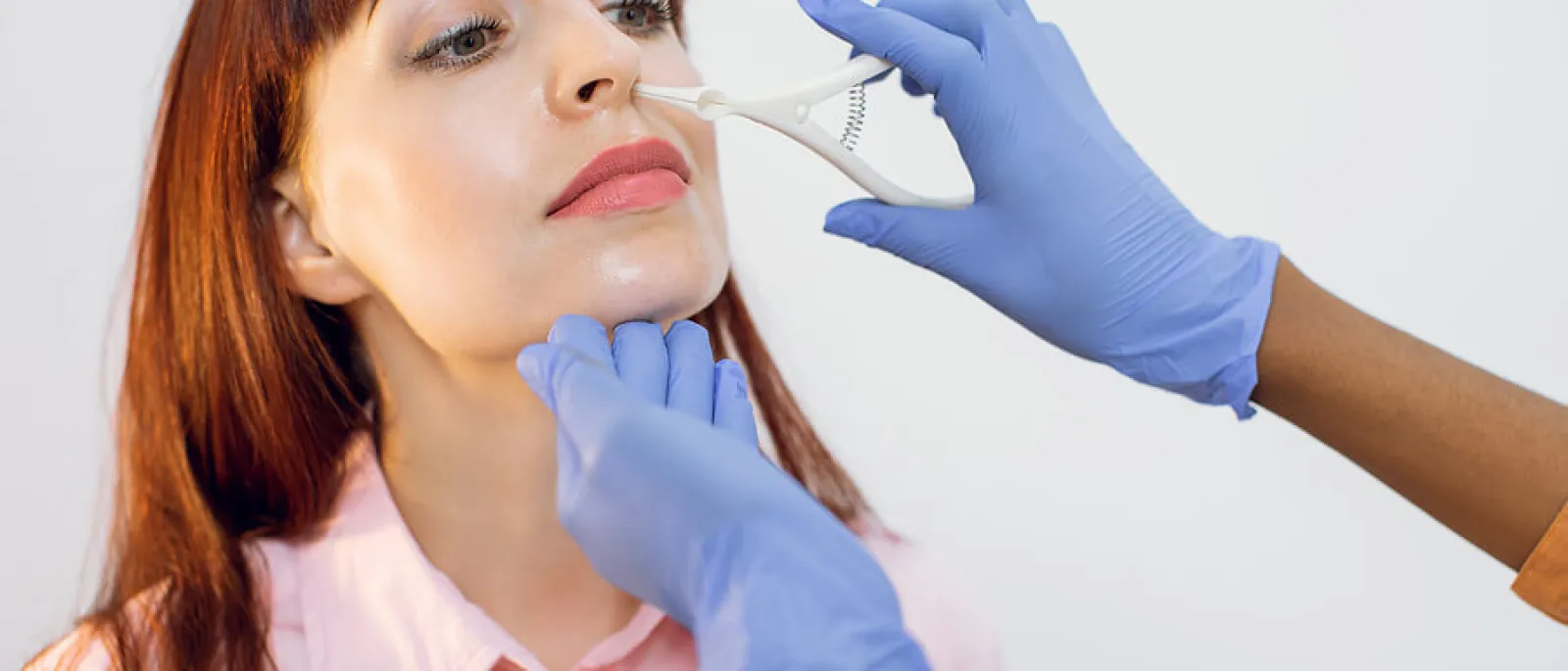
The nasal turbinate
refers to vital parts of the anatomy inside the nose that stop dirt and other
particles from entering the trachea and lungs. Nasal turbinates are minute,
cone-shaped, and are responsible for filtering out debris from the air we
inhale. They regulate airflow and warm and humidify the air we breath. However, when they become enlarged or
inflamed, the body experiences symptoms such as chronic nasal congestion, often
associated with sleep problems, facial pain and headaches, and more frequent
sinus infections.
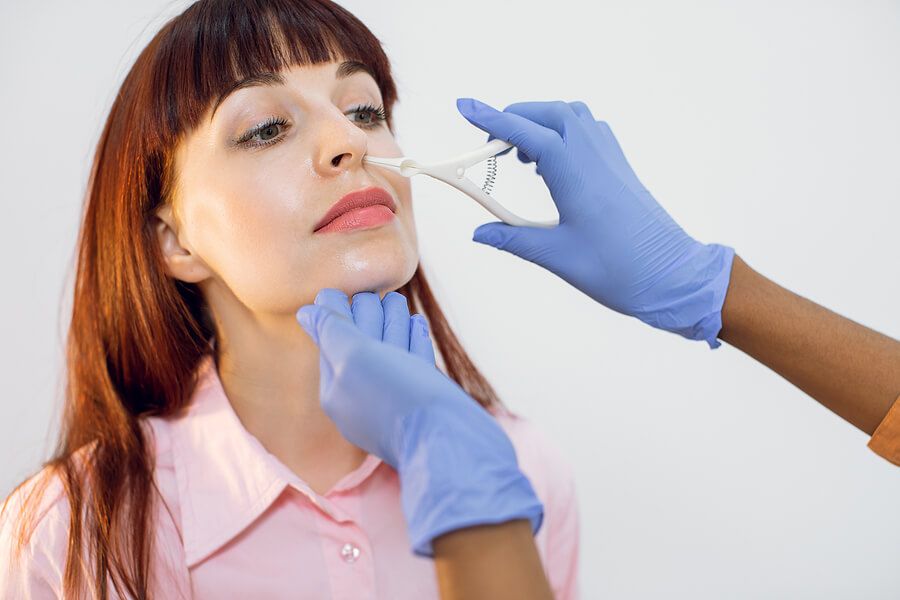
Turbinate reduction procedures
Refers to a surgical procedure performed by ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists to reduce swollen turbinates while improving airflow and preserving the inner linings within the nose. This procedure is necessary when experiencing symptoms of nasal congestion because it helps remove excess tissues around the turbinates and brings about free breathing. There are three types of turbinate reduction prcedures:
-
Laser or radiofrequency office turbinate reductions: Performed under local anesthesia, the laser or radiofrequency device precisely targets and reduces the swollen turbinate. This procedure occurs with topical and local anesthesia. You are not impaired, can drive yourself to and from the appointment, and can potentially return to work the same day.
-
Submucous resection of the turbinates: Usually performed as an outpatient procedure under anesthesia. This involves using a surgical instrument that removes excess from inside the turbinate to reduce it's volume and improve nasal breathing. Patients can usually return to work in a couple of days.
It is also common for
septoplasty and turbinate reduction
to be performed together if the patient has a deviated septum as well.