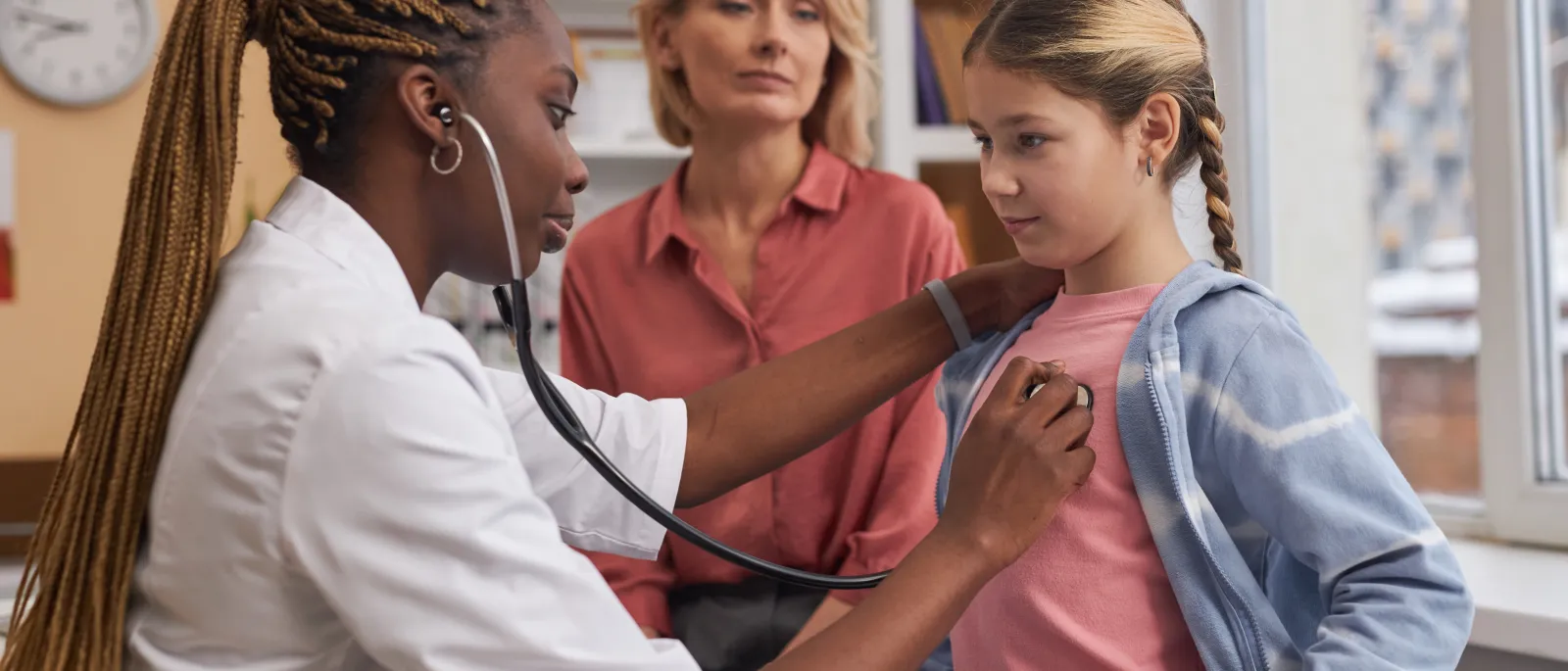
- Understanding the causes and treatments for chronic cough in children.
- Practical tips on how to stop a constant cough in child effectively.
- When to seek professional help for a child cough won't go away.
A chronic cough can be worrisome, mainly when it affects your child. If your child cough won't go away, it's crucial to understand the potential causes and treatments available. This blog will provide comprehensive tips for managing a chronic cough in children and help you determine when to seek professional medical advice.
Understanding Chronic Cough
A persistent cough in child with no other symptoms can be challenging to diagnose. Chronic cough is defined as a cough lasting more than four weeks. Identifying the underlying cause is essential to treating it effectively. Here are common causes of chronic cough in children:
- Postnasal Drip: Often due to allergies or sinusitis, leading to throat irritation. Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger this condition.
- Asthma: Characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, asthma can cause a chronic cough, especially at night or after physical activity. Common symptoms include wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Respiratory Infections: Infections like whooping cough (pertussis) or chronic bronchitis can result in a persistent cough. These conditions may require antibiotics or other treatments.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD happens when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, causing irritation and a chronic cough. Symptoms often include heartburn and regurgitation.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to secondhand smoke, pollution, or strong odors can lead to a chronic cough. Reducing exposure to these irritants is crucial for managing symptoms.
How to Stop a Constant Cough in Child
Managing a chronic cough requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some tips to help alleviate your child's symptoms:
- Ensure Adequate Hydration: Keeping your child well-hydrated can thin mucus and soothe an irritated throat. Encourage them to drink water, herbal teas, or warm broths. Avoid caffeinated or sugary beverages, as they can lead to dehydration.
- Use a Humidifier: Using a humidifier increases the moisture level in the air, which can help calm an irritated throat and loosen mucus. This is particularly advantageous during the dry winter season. Regularly clean the humidifier to prevent mold and bacteria buildup.
- Address Allergies: If allergies are the cause, reducing exposure to allergens is crucial. Keep windows shut during peak pollen seasons, use air purifiers, and wash bedding regularly. Over-the-counter antihistamines or prescribed allergy medications can also be effective.
- Try Honey: For children over one year old, honey can be a natural cough suppressant. A spoonful of honey before bed can reduce nighttime coughing. Avoid giving honey to children under one year old because of the risk of botulism.
- Elevate the Head: Elevating your child's head while they sleep can help reduce coughing caused by postnasal drip or GERD. Use extra pillows or elevate the mattress. This position helps prevent mucus from pooling in the throat.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam can aid in opening up the airways and loosen mucus. A hot shower or steam from a bowl of hot water can provide relief. Enhancing the effect with a few drops of eucalyptus oil can provide additional relief.
Persistent Cough in Child with No Other Symptoms Treatment
When a cough persists without other symptoms, it's important to consider underlying conditions like asthma or GERD. Here are some targeted treatments:
Asthma
If asthma is suspected, a doctor may prescribe inhalers or other medications to manage the condition. Regular monitoring and avoiding triggers are key to control. Long-term management may include corticosteroids or bronchodilators.
GERD
For GERD, dietary changes and medications can help manage symptoms. Avoiding spicy, fatty, or acidic foods before bed can reduce nighttime coughing. Medications such as antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed.
Postnasal Drip
Treatment may include antihistamines or nasal sprays to reduce mucus production and alleviate throat irritation. Saline nasal rinses can also be effective in clearing nasal passages.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many coughs can be managed at home, it's important to know when to seek medical advice. Contact a healthcare provider if your child experiences:
- A cough lasting more than four weeks.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- High fever or persistent low-grade fever.
- Weight loss or fatigue.
- Coughing up blood.
- Sudden onset of a severe cough.
Managing a chronic cough in children requires understanding the underlying causes and implementing effective treatments. By following these tips and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can help your child find relief and improve their quality of life. If your child cough won't go away, don't hesitate to reach out to ENT of Georgia South for expert guidance and care. Visit our website to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists.

